Data Governance and Analytics
Rinse and Repeat
Utility companies today face a significant challenge: insufficient data about their assets. Much of the infrastructure was built decades ago, during a time when data collection was not prioritized for operational efficiency. As a result, utilities now face the task of bridging this data gap.
The good news is that with the advent of smart meters and other advanced data sources, utilities have access to a wealth of new, real-time information. However, to fully unlock the potential of this data, utilities must embrace a data-driven environment that supports their systems, processes, and workforce.
To support the transformation of your operations, we leverage our proprietary Rinse and Repeat Methodology™. This methodology is built on a clear roadmap and established standards designed to optimize data efficiency. By adopting this approach, utilities can move beyond legacy models and create real-time, accurate representations of their networks. This transformation empowers utilities with the ability to make data-driven decisions, enhance grid management, and drive significant improvements in operational efficiency.

Concept
- Cycle of Improvement: This methodology involves continuously repeating a set of steps to achieve incremental improvements and refine processes.
Steps:
1.Plan: Identify objectives and plan the actions needed to achieve them.
2.Execute: Implement the planned actions.
3.Review: Assess the results and identify areas for improvement.
4.Adjust: Make necessary adjustments based on the review.
5.Repeat: Start the cycle again with the adjusted plan.
Benefits:
- Continuous Improvement: Regularly refining processes leads to better outcomes over time.
- Flexibility: Allows for adjustments based on feedback and changing conditions.
- Simplicity: Easy to understand and implement, making it suitable for various contexts.

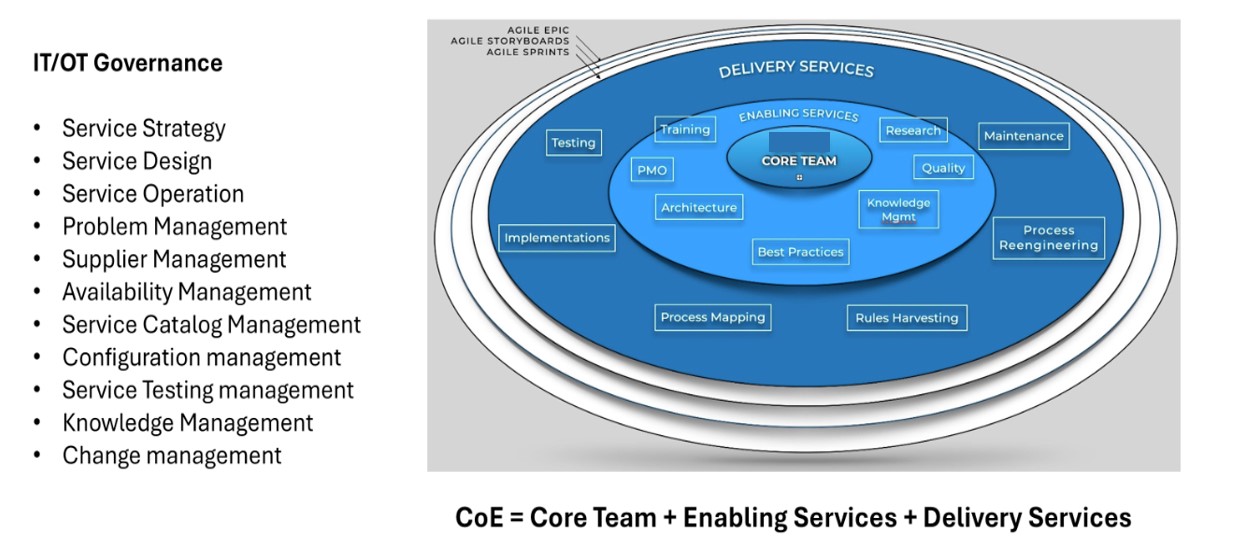
Overview
A data governance framework ensures the integrity, security, and compliance of data within utility companies.
Key Components:
1.Data Stewardship: Assign data stewards to maintain data accuracy and compliance.
2.Data Quality Management: Implement processes to ensure high data quality.
3.Data Management: Define how data is created, stored, accessed, and shared.
4.Technology Infrastructure: Use robust systems like databases and ERP.
5.Data Privacy and Security: Ensure compliance with privacy laws and protect data from security risks.
Benefits:
- Regulatory Compliance: Adhere to laws like HIPAA and GDPR.
- Improved Data Quality: Standardize data management practices.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: Provide reliable data for strategic planning.